Ready to learn more?

Explore More

Bryan Strike, MS, MTx, CFA, CFP®, CPA, PFS, CIPM, RICP®
Director, Financial Planning
Converting a traditional IRA into a Roth IRA can provide tax savings now and in the future. Here’s what you need to know in 2024.

A strategic approach to a Roth conversion can result in tax savings, increased potential asset growth, and estate-planning advantages. Read on to learn more about the benefits for people nearing retirement, already retired, and for their heirs.
Established in 1997 and named after former Delaware Sen. William Roth, Roth IRAs are funded with after-tax dollars while contributions to a traditional IRA generally qualify for a tax deduction. However, Roth IRA balances are not subject to taxation, all future withdrawals are also generally tax-free, and Roth IRA holders do not have to take a required minimum distribution (RMD) from their account each year. By contrast, withdrawals from a traditional IRA are treated as taxable income and the account holder must take a yearly RMD starting at age 73. Additional information on the taxability of Roth IRA distributions can be found here.
Because of these key distinctions, a Roth conversion can be advantageous for people with large traditional IRA balances who expect to pay as much or more income tax in retirement as they are paying now. One of the best times to convert IRA dollars to a Roth IRA is during what is referred to as “the trough years” – the period after you’ve retired but before you’re subject to RMD rules.
When making a Roth conversion, the tax is paid on retirement savings today, in exchange for tax-free growth for the future. As shown below, conversions made during “trough years” can allow a person to remain in a lower tax bracket, avoid a larger tax bill, and help ensure future RMDs won’t be subject to higher tax rates.
Implementing Systematic Roth Conversions
Remain in lower tax brackets, avoiding higher tax rates today, while helping to ensure your future RMDs won’t be subject to higher tax rates when you retire.
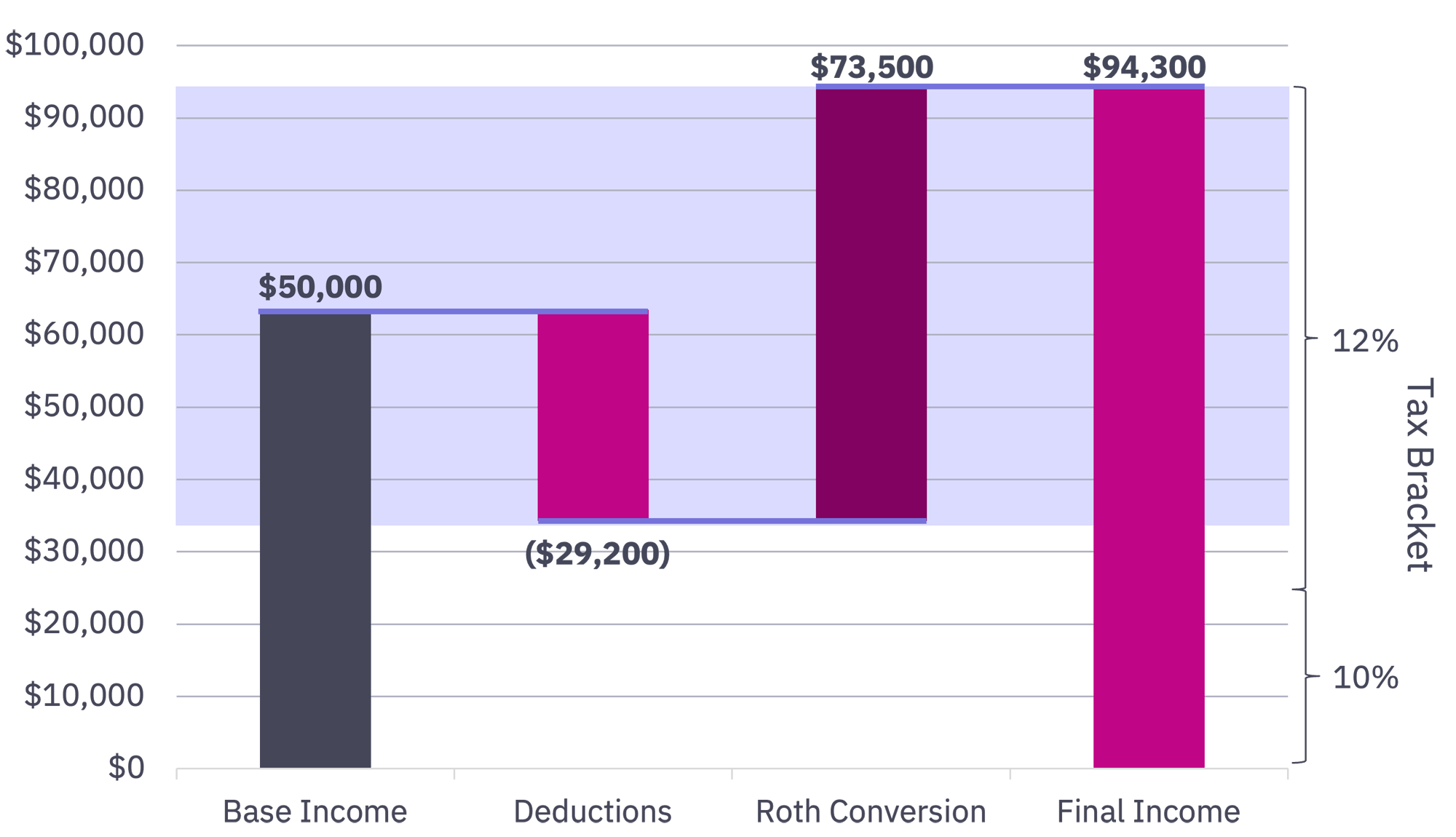
Performance quoted is past performance and is not indicative of future results. For Illustrative Purposes Only. Source: www.kitces.com.
Long-Term Value of Proactive Roth Conversions
Converting annual growth of IRA reduced future required minimum distributions.
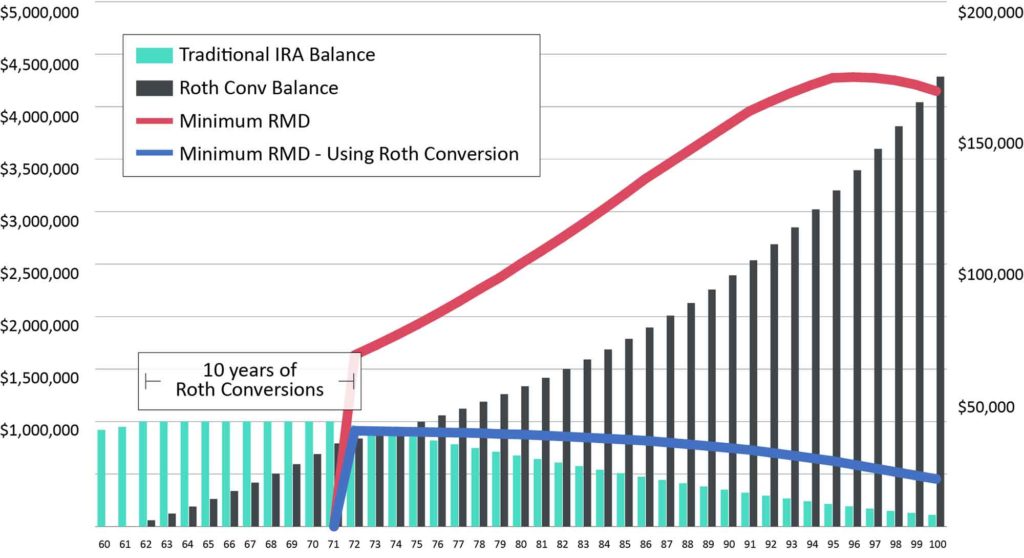
Performance quoted is past performance and is not indicative of future results. Assumes IRA balance of $1M at age 60 with 6% growth year-over-year. Roth conversions occur from 62 years old to 72 years old and assumes all IRA growth is converted to the Roth on an annual basis. For Illustrative Purposes Only.
As a result of converting $60,000 — equivalent to 6% annual growth in the traditional IRA balance — to a Roth IRA each year from ages 62 to 72, the retiree in this hypothetical example would have a balance of more than $2 million at age 85. This is possible because the person can let their Roth IRA grow tax-free while relying on RMDs from their traditional IRA as income. If left untouched, the Roth IRA balance in this example would reach nearly $5 million by the time the retiree was 100.
The Setting Every Community Up for Retirement Enhancement Act (SECURE) Act, which took effect in 2020, significantly changed some inherited IRA rules for non-spouse beneficiaries. For beneficiaries who inherited when the account holder died after Jan. 1, 2020, the SECURE Act requires the balance of the participant’s inherited IRA account to be distributed or withdrawn by the end of the 10th year following the original owner’s death (with some exceptions). A Roth conversion helps ensure that the inherited retirement account balance is tax-free — relieving beneficiaries of the income impact from the 10-year withdrawal requirement.
It does, in specific situations. Let’s say you have a traditional IRA that you’ve been paying into for years. Once you retire, you and your spouse begin drawing Social Security in one year and have income from savings and investment account withdrawals. This combination may put you into a higher tax bracket and any IRA withdrawals will then be taxed at a higher rate. Converting a traditional IRA to a Roth IRA will help reduce your overall tax burden.
Let’s look at another example of a married couple with a base income of $110,000. When they must start RMDs, they are projected to include $60,000 on top of their other income. Instead of waiting to start RMDs, if they move that $60,000 to a Roth IRA, their taxable income is still going to be $170,000 but that money can continue to grow tax-free, unaffected by future required distributions.
If you’re considering a Roth IRA conversion, it’s important to weigh the current factors that apply to your specific situation as well as how things may change during your retirement. For personalized advice, contact your wealth advisor. If you’re not already a Mercer Advisors client, let’s talk.
Mercer Advisors Inc. is a parent company of Mercer Global Advisors Inc. and is not involved with investment services. Mercer Global Advisors Inc. (“Mercer Advisors”) is registered as an investment advisor with the SEC. The firm only transacts business in states where it is properly registered or is excluded or exempted from registration requirements.
All expressions of opinion reflect the judgment of the author as of the date of publication and are subject to change. Some of the research and ratings shown in this presentation come from third parties that are not affiliated with Mercer Advisors. The information is believed to be accurate, but is not guaranteed or warranted by Mercer Advisors. Content, research, tools, and stock or option symbols are for educational and illustrative purposes only and do not imply a recommendation or solicitation to buy or sell a particular security or to engage in any particular investment strategy. Past performance may not be indicative of future results. All investment strategies have the potential for profit or loss. Different types of investments involve varying degrees of risk, and there can be no assurance that any specific investment will either be suitable or profitable for a client’s investment portfolio. Hypothetical examples are for illustrative purposes only. For financial planning advice specific to your circumstances, talk to a qualified professional at Mercer Advisors.
Certified Financial Planner Board of Standards, Inc. (CFP Board) owns the CFP® certification mark, the CERTIFIED FINANCIAL PLANNER® certification mark, and the CFP® certification mark (with plaque design) logo in the United States, which it authorizes use of by individuals who successfully complete CFP Board’s initial and ongoing certification requirements.

